The World Population Review report notes that Indonesia is a country with the fourth largest population in the world, which has a strategic location, developed infrastructure, and a wealth of natural resources. This condition certainly makes Indonesia one of the countries that has great potential in the transportation and warehousing sector.
The World Population Review report notes that Indonesia is a country with the fourth largest population in the world, which has a strategic location, developed infrastructure, and a wealth of natural resources. This condition certainly makes Indonesia one of the countries that has great potential in the transportation and warehousing sector.
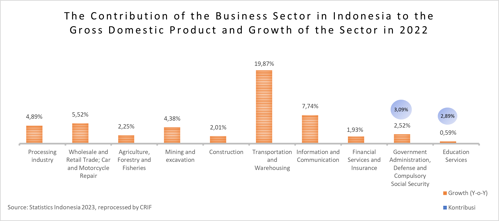
Data from Statistics Indonesia (BPS) shows that the contribution of the transportation and warehousing sector to gross domestic product (GDP) is 5.02% in 2022, or is the sector that has the 6th largest contribution after the manufacturing industry, large and retail trade, repair cars and motorbikes, agriculture, forestry and fishing, mining and quarrying, and construction. However, based on growth data, the transportation and warehousing sector recorded the highest rate of 19.87% year-on-year (Y-o-Y).
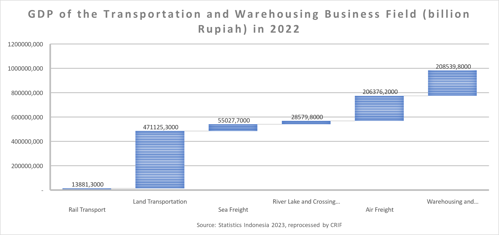
Based on the table above, it can be seen that the sub-sector that contributed to the transportation and warehousing sector to the largest gross domestic product (GDP) was the land transportation sub-sector which exceeded IDR 471.1 trillion, followed by the warehousing and transportation support services sub-sector; postal and courier services of IDR 20.5 trillion in 2022. This condition is in line with the government's encouragement to revive national economic performance and increase community mobility by easing restrictions on community activities.
The increase in the army sub-sector was influenced by increased consumer mobility at the national level, one of which is reflected in Traveloka's internal data regarding the trend of users traveling by bus, where there has been an increase in bookings on new routes not only in big cities on the island of Java and Sumatra, but also saw a positive trend in Sulawesi. Several big cities such as Surabaya, Semarang, Yogyakarta, Malang, Bandung are still favorite destinations. As for the island of Sumatra, Bandar Lampung, Palembang, Medan, Padang and Pekanbaru are also options. Interestingly, this positive trend can also be seen in other cities such as Makassar, Tana Toraja, and Mamuju. This shows that the strong digital penetration and the use of technology have begun to spread to other regions so that more and more people are experiencing the convenience of ordering buses online. (Mediaindonesia.com, 2022)
The sub-sector that has the second largest contribution to the gross domestic product (GDP) in the transportation and warehousing sector is the warehousing and transportation support services sub-sector; post and courier. This sub-sector is considered to have an important role for various other business sectors, including:
· E-commerce: Logistics is very important in e-commerce operations, especially when it comes to product delivery. Many e-commerce companies rely on third-party delivery services to deliver goods to their customers.
· Manufacturing: Logistics is critical in shipping raw materials, shipping finished products, inventory management, and shipping products to customers. Manufacturing companies often rely on logistics services to optimize their supply chain.
· Retail: Retail is a business sector that relies heavily on logistics, especially in terms of inventory management and the delivery of products from distribution centers to stores.
· Transportation: Logistics is at the core of the transportation business, from local to international shipping
· Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, logistics is very important when it comes to the delivery of drugs, medical devices and medical equipment from manufacturers to medical institutions or pharmacies.
· Agriculture: Logistics is important in the delivery of raw materials and agricultural products, such as the delivery of fruit and vegetables from farmers to markets or the delivery of animal feed from factories to farms.
· Mining: Logistics are important in the transportation of mining materials from the mine to the processing plant and the shipment of finished products from the factory to the customer.
Logistics Sector Performance Projection for 2023
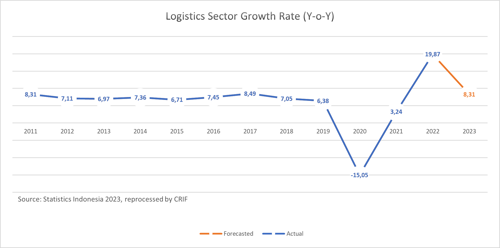
The BPS report shows that the growth rate of the logistics sector in 2020 is minus 15.05% and will continue to increase until the end of 2022 to 19.87%. CRIF projects that the logistics sector in 2023 will record a growth rate of 7 percent to 9 percent (Y-o-Y). CRIF also predicts that the logistics sector's contribution to gross domestic product (GDP) in 2023 will be around IDR 1,065.1 trillion after previously IDR 983.5 trillion in 2022. This projection is made taking into account Indonesia's estimated economic growth of 5.16% in 2023 and the political factors that influence it.
The slowdown in the growth of the logistics sector in 2023 is related to the threat of recession and uncertainty in global supply chains, including as a result of global geopolitical dynamics. However, if there are a number of strategies in the logistics sector, positive growth can be achieved. This prediction is also in line with projections from Kadin and the Indonesian Logistics Association which also see that the logistics business in 2023 is still good, especially with the start of normal economic activity and the absence of Large-Scale Social Restrictions (PSBB), so that the activities of companies have also started return to normal (Swa.co.id, 2023). According to a report from Research and Markets, it is expected that the growth of Indonesia's logistics sector will reach a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) from 2020 to 2025. This is driven by increasing demand for logistics in Indonesia, especially in the e-commerce sector, as well as support from the government in developing logistics infrastructure throughout the country.

In addition, the high cost of logistics is a burden, especially for the manufacturing industry. This will affect the competitiveness of the industry in producing goods or services. Furthermore, it also has an impact on macroeconomic performance. And one of the big challenges in the logistics sector is the uneven distribution of connectivity infrastructure. The development of infrastructure connectivity in Indonesia by prioritizing logistics cost efficiency is very important. Therefore, the flow of logistics distribution in Indonesia is influenced by geographical conditions and various environmental characteristics, as well as the uneven development of infrastructure and infrastructure.
The Role of Logistics in the E-Commerce Sector
The e-commerce sector is expected to continue to grow rapidly due to the increasing number of internet users and smartphone users in Indonesia. In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic has also accelerated the adoption of e-commerce by Indonesians, resulting in an increase in online transactions.
It is undeniable that the increasing number of people doing online shopping transactions will be in line with the increasing demand for shipping goods so that the logistics sector will continue to develop to adapt to market needs. The logistics sector plays a key role in delivering products purchased online to customers quickly and efficiently. To be able to meet this demand, logistics companies must increase capacity and efficiency in managing the supply chain, starting from warehouses, packaging, to delivery.

The E-Commerce sector is the largest contributor to the digital economy in Indonesia. The sector grew rapidly during the pandemic. And the e-commerce sector is projected to continue growing by almost two folds in 2025 compared to 2022.
In addition, data from Bank Indonesia (BI), based on projected e-commerce transactions in November 2022, e-commerce transactions are expected to reach IDR 572 trillion. The Indonesian e-Commerce Association (idEA) assesses that e-commerce will still be a pillar of the Indonesian economy in 2023, following the sector's continued dominance in the growth of the national digital economy. (Katadata.co.id, 2023). Increasing the e-commerce sector can also trigger technological developments in the logistics sector, such as using an automated tracking and delivery system that can help speed up and facilitate the delivery of goods. Thus, the logistics sector will progress and develop, so that it can meet market demand and increase efficiency in shipping goods as a whole.
According to a report on e-commerce in Indonesia, the increase in Indonesia's e-commerce GMV is in line with the increasing population of digital consumers in the country. The B2C e-commerce market in Indonesia is expected to grow steadily, with a CAGR of 15.56% between 2022-2026, and is expected to become one of the largest digital economies in Southeast Asia, with 40% regional market share. (Prnewswire.com, 2022)
Logistics Sector Challenges in 2023
Even though it is predicted to grow in 2023, business players in the logistics sector must be aware of the issue of a recession. CRIF assesses that the threat of a global recession will have an impact on the performance of the logistics sector in 2023. A recession can cause a decrease in demand from consumers and businesses, thereby reducing the amount of goods transported by the logistics sector. In addition, a recession can also affect the ability of logistics companies to meet operational costs and pay employees, which can affect the performance of the logistics sector as a whole. However, the impact of the recession issue on the performance of the logistics sector will depend on various factors such as how severe the recession is, how quickly the economy can recover, and how business players in the logistics sector can adapt to difficult situations. Moreover, the logistics sector can also take advantage of technology and innovation to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs, thereby overcoming some of the negative effects of the recession.
