The Information and Communication Technology (ICT) industry is on the brink of a major revolution heading toward 2025. Various sectors are poised to undergo significant transformations with rapid technological advancements such as 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain.
This article explores Indonesia's prospects, challenges, and opportunities in the evolving ICT landscape, emphasizing solutions for inclusive and sustainable development. By connecting global technological advancements with localized insights from CRIF Indonesia, it analyzes how innovations in technology can transform business operations, strengthen cybersecurity, and drive digital transformation. Furthermore, it offers actionable strategies tailored for policymakers and ICT industry leaders, advocating a strategic and data-informed approach to shaping the future.
Digital Transformation in Business Sectors
Digital transformation has become a top priority for companies, especially following the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated the adoption of digital technologies. According to a Deloitte report (2023), 60% of global companies have integrated AI into their business processes. However, in Indonesia, this figure stands at just 35%.
Data reveals significant fluctuations in indicators reflecting the adoption and impact of digital transformation in business sectors from 2019 to 2024. A steady growth trend was observed from Q1 2019 to Q4 2020, peaking at 10.99% in Q4 2020, driven by accelerated digitalization during the pandemic. However, a sharp decline followed from Q1 2021 to Q3 2021, hitting a low of 5.54% in Q3 2021. This drop underscores the substantial challenges businesses face in maintaining digitalization momentum.
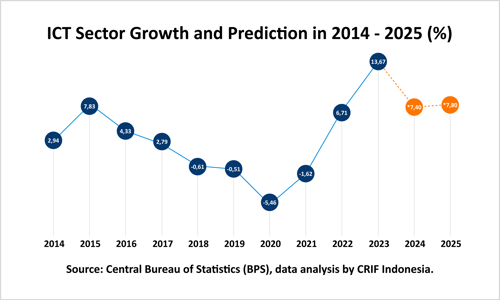
Recovery began in Q4 2021 and continued through Q2 2022, with figures rebounding to 8.06% in Q2 2022. Despite this, fluctuations in Q3 2023 (8.51%) and Q4 2023 (6.74%) highlight persistent challenges in stabilizing digital transformation. These challenges likely stem from imbalances between adopting new technologies and preparing human resources.
CRIF Indonesia forecasts that Indonesia's ICT sector will experience continued positive growth in Q4 2024 and beyond into 2025, with an estimated annual growth rate of approximately 7%. This projection is based on the widespread adoption of technologies such as AI, IoT, and 5G, enhanced digital infrastructure, and increased integration of technology-driven solutions across industries. Additionally, government initiatives to promote digital transformation are expected to position the ICT sector as a key driver of Indonesia's digital economic growth.
"Businesses must prioritize digital training and invest in infrastructure that supports sustainable technology integration," stated a CRIF analyst. With strategic approaches, companies can not only adapt but also create added value amid digital transformation challenges.
Global ICT Market Outlook for 2025
The global ICT market is projected to reach USD 5.74 trillion by 2025, driven by significant growth in software and cloud-based services. Gartner estimates that global IT spending will rise by 9.3% in 2025 compared to 2024, reaching USD 5.74 trillion (Source: Techzine).
In Indonesia, cloud computing penetration is expected to grow to 75%, fueled by increased demand for digital transformation across public and private sectors. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 75% of all data will be generated outside traditional data centers and cloud environments (Source: Forbes).
CRIF Indonesia emphasizes that these opportunities enable local companies to focus on developing cloud solutions that enhance productivity and operational efficiency. The rise of cloud technology adoption in Indonesia not only benefits the tech sector but also positively impacts industries reliant on digitalization. CRIF underscores the importance of collaboration between the private sector, government, and cloud service providers to accelerate the adoption and implementation of cloud-based solutions. Through supportive policies, the government can help create a more conducive ecosystem for rapid and efficient digital technology adoption.
Internet User Growth in Indonesia 2024 and ICT Prospects for 2025
By 2024, Indonesia's internet user base is projected to exceed 200 million, reflecting a rapid uptake of digital technologies across all societal levels. This growth is driven by improved digital infrastructure, more affordable data services, and the proliferation of internet-enabled devices such as smartphones and IoT devices. According to the Indonesian Internet Service Providers Association (APJII), approximately 70% of Indonesia's population will be online by 2024.
This surge opens immense potential for the ICT sector, which is expected to thrive in 2025. Key trends include the adoption of 5G technology enabling faster internet speeds, the expansion of e-commerce driven by a growing online consumer base, and the widespread implementation of IoT across sectors like agriculture and manufacturing. The rising dependence on the internet will also amplify the demand for cybersecurity solutions.
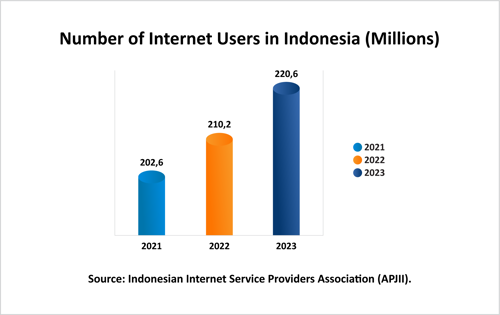
CRIF Indonesia notes that increased internet penetration significantly impacts sectors such as e-commerce, digital finance, and education. With over 200 million internet users by 2024, CRIF sees a vast opportunity for businesses to expand their markets and drive technology adoption. However, CRIF highlights the critical need for data security and privacy, given the escalating threats to digital transactions and personal information. To maximize these opportunities, businesses and the government must collaborate to build a safer and more inclusive digital infrastructure.
Regulatory Challenges and Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity remains a critical issue in the digital era. Check Point Research (2024) reports a 38% global increase in cyberattacks compared to the previous year. Indonesia, one of the world's largest internet user bases, is a prime target for these attacks.
The Indonesian National Cyber and Encryption Agency (BSSN) recorded a significant rise in cyberattacks in recent years:
-
2021: 266.74 million attacks, with over 60% involving malware and ransomware, primarily targeting government and public service sectors (Source: Kominfo).
-
2022: 370 million attacks, a 38.7% increase, with financial and e-commerce sectors witnessing a surge (Source: Kominfo).
-
2023: 403 million attacks, with critical infrastructure sectors like energy and transportation becoming major targets (Source: MetroNews).
This data highlights the severity of cybersecurity threats faced by Indonesia, with trends indicating a consistent annual increase.
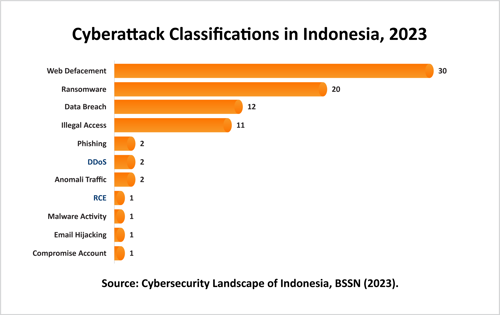
Analyzing cybersecurity incidents in Indonesia reveals that the most frequent types of attacks include:
-
Web Defacement: Altering website appearances maliciously.
-
Ransomware: A type of malware that locks users out of their systems until a ransom is paid.
-
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Among the most impacted sectors is the government, which remains a prime target for these attacks, underscoring the urgent need for robust defense measures.

In mid-2024, the Indonesian government faced alarming ransomware attacks on the National Data Center (PDN). The attacks, using Lock Bit 3.0 Brain Cipher variants, began on June 17, 2024, causing disruptions to central and regional government services and encrypting vital PDN data.
Cybersecurity challenges continue to evolve alongside rapid technological changes. A holistic and collaborative approach involving the government, private sector, and society is essential to fortify Indonesia's cyber defense systems. Key measures include upgrading security infrastructure, regular system updates, and leveraging advanced technologies to prevent data breaches and protect online transactions. Additionally, education and training are critical to raising public awareness about data protection and online safety. Comprehensive and accessible training programs can help mitigate cyber threats effectively.
Given the global nature of cybercrime, international collaboration is also crucial. Indonesia must strengthen partnerships with other nations to combat foreign-origin cyberattacks through information and technology exchange.
CRIF Indonesia’s Recommendations for a Resilient Digital Future
CRIF Indonesia concludes that securing Indonesia's digital ecosystem demands unwavering commitment from all stakeholders. Proactive investments in advanced technologies, stronger cross-sectoral collaborations, and comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks are essential to building resilience against emerging threats. By adopting these strategies, Indonesia can not only mitigate risks but also unlock the full potential of its digital economy, creating a more secure and prosperous future for all.
CRIF further recommends prioritizing education and digital literacy at every level to prepare a skilled workforce capable of managing emerging technologies. Businesses should also adopt a proactive stance by conducting regular cybersecurity audits, fostering public-private partnerships, and investing in predictive analytics to stay ahead of potential threats. Meanwhile, policymakers must craft adaptive regulations that balance innovation with safety, ensuring a robust yet flexible digital ecosystem. Together, these efforts will pave the way for a resilient, innovative, and digitally empowered Indonesia.

