The tobacco industry in Indonesia has long been a cornerstone of the economy and a part of cultural identity, contributing approximately 135.754 trillion IDR to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2022 and 2023. However, it now faces a critical crossroads. Major disruptions are arising from the implementation of Government Regulation No. 28 of 2024, which introduces strict restrictions, such as prohibiting cigarette advertising on many platforms except in designated areas regulated by the government and banning cigarette sales near schools and child-frequented locations. With cigarette production plummeting to a record low of 318.1 billion sticks in 2023, the industry must rapidly adapt amid growing public health awareness.
Hence, the tobacco industry confronts increasingly complex challenges, including potential job reductions and the need for product diversification, necessitating innovative strategies to remain relevant and sustainable while complying with stricter health policies. Will the industry survive and transform, or will it collapse under the storm of regulatory pressures?
Trends in Cigarette Production
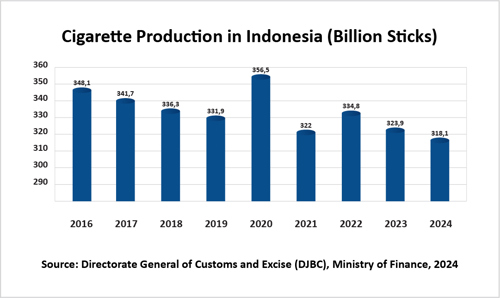
Data from the Ministry of Finance reveals a general downward trend in cigarette production in Indonesia from 2015 to 2023. Despite a significant increase in 2019, production sharply declined the following year. By 2023, production reached a low of 318.1 billion sticks. This decline reflects the impact of smoking consumption control policies and a shift in public preferences toward recognizing the negative health effects of smoking. The government's excise tax policies and strict regulations have also contributed to this decline, potentially affecting manufacturers and tobacco farmers. In 2024, the implementation of Government Regulation No. 28 is expected to further decrease the performance of the tobacco industry.
Data on the growth of the tobacco processing industry, average cigarette tax increases, and contributions to GDP from 2012 to 2023 paint a complex picture of this industry in Indonesia. In 2012, the industry experienced robust growth with a rate of 8.82%, driven by stable demand and effective marketing strategies. However, over time, this growth has seen fluctuations. The year 2013 recorded near-stagnation with a growth rate of -0.27%, coinciding with an excise increase of 8.50%. Continued tax hikes in subsequent years exerted additional pressure on the industry, creating a dilemma between public health policies and the survival of the tobacco sector. For example, in 2020, the excise tax rose by 23%, leading to a significant decline in industry growth to -5.78%. This indicates that drastic tax increases directly impact consumer purchasing power and market demand.
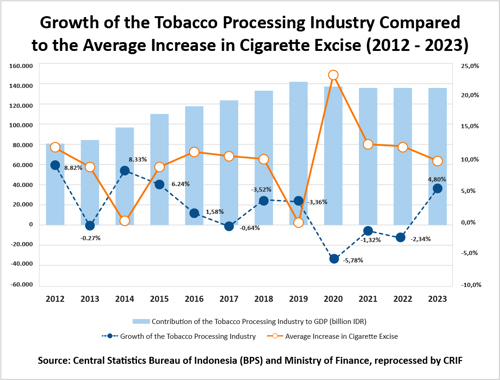
Conversely, while the contribution of the tobacco processing industry to GDP remains relatively stable—from 79.34 trillion IDR in 2012 to approximately 135.754 trillion IDR in 2022 and 2023—the sustainability of this industry faces serious challenges. In 2021 and 2022, despite ongoing excise increases, industry growth remained suppressed with negative figures of -1.32% and -2.34%, respectively. This suggests that the tobacco industry must adapt to increasingly stringent regulations and enhance product innovation to stay competitive in the market. With changing consumer behavior prioritizing health and safety, the tobacco processing industry must seek alternatives, whether through product diversification or more innovative marketing approaches, to sustain operations and contributions to the national economy.
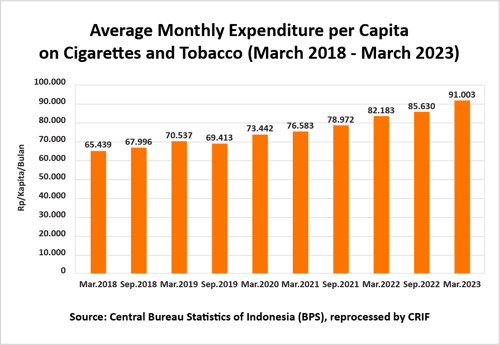
The Central Statistics Bureau of Indonesia (BPS) notes that monthly per capita cigarette expenditures have consistently increased year-on-year. Data indicates that per capita cigarette expenditure reached 91,003 IDR as of March 2023, a 6.3% increase from 85,630 IDR in September 2022. The proportion of per capita expenditure on cigarettes and tobacco stands at 12.8% among food groups, making it the second largest share after food and beverage commodities.
With tens of millions of consumers, it is no surprise that cigarettes significantly influence Indonesia's inflation. According to BPS data, cigarettes consistently rank among the top five contributors to inflation each year.
No Increase in Cigarette Excise Tax in 2025
Cigarette excise tax is a significant source of government revenue in Indonesia. Each year, the decision to raise cigarette excise tax receives scrutiny due to its implications for state revenue, the tobacco industry, and public welfare. However, recent analyses indicate that cigarette excise tax will not increase in 2025. This decision follows the latest discussions with the House of Representatives (DPR) and considerations regarding the 2025 State Budget (APBN). Although the tobacco excise tax rate will remain unchanged, the government plans to adjust the retail selling price (HJE) of tobacco products in 2025. This decision is seen as a breath of fresh air for the continuously pressured tobacco industry.
The Director General of Customs and Excise at the Ministry of Finance, Askolani, confirmed that tobacco excise tax rates would not increase in 2025. This decision considers the outcomes of the recently approved 2025 State Budget by the DPR (CNBC Indonesia, September 27, 2024). One of the reasons for maintaining the current cigarette tax policy in 2025 is the emergence of a phenomenon known as down trading, where consumers switch to cheaper cigarette products.
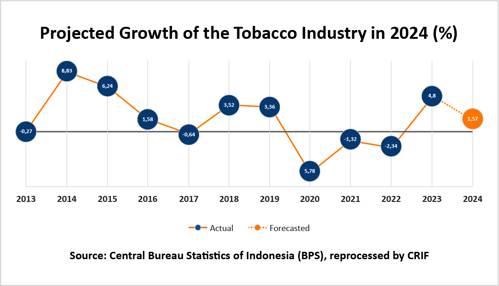
The diagram above illustrates the growth rate trends from 2013 to 2023 and predictions for 2024. These growth figures serve as indicators for predicting state revenue potential from various sectors, including excise taxes. From 2013 to 2023, significant fluctuations in growth are apparent, with years like 2014 and 2015 recording relatively high growth rates of 8.33% and 6.24%, respectively. However, other years, particularly 2020 and 2022, showed substantial declines of -5.78% and -2.34%. These declines coincided with various economic challenges, including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
Positive Growth in 2023 and Predictions for 2024
In 2023, the industry experienced recovery with a growth rate of 4.8%, indicating an economic improvement after previous challenges. Predictions for 2024 suggest a growth rate of 1.57%, slightly slower than the previous year. This figure reflects expected stability, albeit with modest growth.
From the available economic growth data, it can be concluded that the decision not to raise cigarette excise taxes in 2025 is aimed at maintaining economic stability and reducing the burden on the tobacco industry. However, it is essential to recognize that this decision carries complex implications for state revenue, industry sustainability, and public health. The government must develop balanced policies, considering broader economic and social impacts to ensure that this decision does not lead to future problems, particularly concerning public health and the national budget.
Implications of Government Regulation No. 28/2024 on the Tobacco Industry
Government Regulation No. 28/2024 is part of the implementation of Law No. 17 of 2023 on Health, aimed at mitigating the negative health impacts of smoking. The implementation of this regulation is inseparable from the need to protect the younger generation and reduce smoking prevalence among the population. In this context, Government Regulation No. 28/2024 contains several key points that could reshape the tobacco industry landscape in Indonesia:
-
Stricter Advertising and Promotion
Cigarette advertising is banned on various platforms, except in government-regulated areas. This forces cigarette manufacturers to find new ways to market their products, potentially affecting brand image and consumer interest, especially among the youth. -
Restrictions on Sales Locations
Cigarettes cannot be sold near schools or locations frequently visited by children. As a result, vendors must adjust their business strategies and seek alternative locations to sell their products. -
Impact on Employment
Stricter regulations may lead to reductions in workforce numbers in the tobacco industry. The government is expected to provide new skills training to help workers transition to more sustainable sectors. -
Agricultural Diversification Programs
Tobacco farmers are encouraged to switch to healthier and more profitable commodities. The government needs to offer incentives and training to ensure a successful transition. -
Challenges for the Tobacco Industry
Rising prices and tighter regulations are causing the cigarette industry to face declining sales and increased production costs. Additionally, the industry must compete with alternative products such as vapes, which are increasingly favored by consumers.
Navigating the Future: Opportunities Amid Challenges
The tobacco processing industry in Indonesia is at a pivotal moment, facing substantial challenges due to the implementation of Government Regulation No. 28/2024. The sharp decline in cigarette production, hitting a record low of 318.1 billion sticks in 2023, underscores the significant impact of smoking consumption control policies and a society increasingly aware of health risks. Although the industry’s contribution to GDP remains noteworthy, at approximately 135.754 trillion IDR in 2022 and 2023, it must navigate new pressures from stricter regulations, such as advertising bans and sales restrictions near schools.
Data indicates that industry growth has experienced fluctuations, with negative figures such as -5.78% in 2020 attributed to drastic excise tax increases of up to 23%. Despite these challenges, CRIF Indonesia believes that the implementation of Government Regulation No. 28/2024 can also present new opportunities for the tobacco industry. Success will hinge on collaboration among the government, industry stakeholders, tobacco farmers, and the public, ensuring that the industry adapts effectively to the evolving landscape while addressing public health concerns.
As per capita cigarette expenditures continue to rise, reaching 91,003 IDR, the industry must innovate and diversify to sustain its relevance and contributions to the national economy while embracing a healthier future.
