The steel industry serves as a fundamental pillar of Indonesia's national development, with its products playing a critical role in a wide range of sectors. Steel's versatility and strength make it an essential material for the construction of transportation infrastructure, including land vehicles (cars, trucks, trains), sea vessels (ships, ferries), and aircraft. Furthermore, steel forms the backbone of infrastructure projects such as bridges, roads, and buildings, ensuring their durability and resilience.
Beyond these core applications, steel serves as a crucial component in the manufacturing of countless other products. From everyday items like appliances and furniture to industrial machinery and equipment, steel's presence is ubiquitous. Its unique properties, including high tensile strength, formability, and recyclability, make it an ideal material for a diverse array of applications.
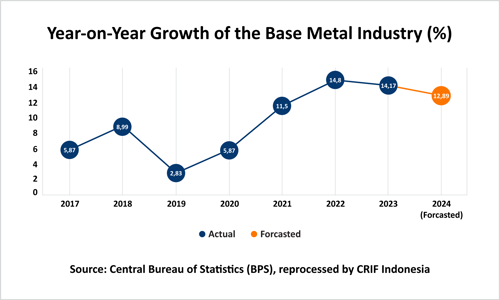
The metal industry continued to demonstrate robust growth in 2023, reaching a rate of 14.17%. This follows a period of stagnation in the precious metals sector between 2019 and 2022, culminating in a peak growth rate of 14.8% in 2022. The 2023 growth was primarily fueled by increased exports, particularly of base metals such as nickel.
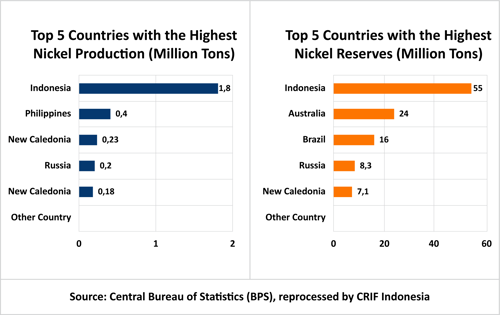
The USGS estimates a 10.1% increase in global nickel production for 2023, reaching 3.6 million tons compared to 3.27 million tons in 2022. Indonesia is expected to dominate with 1.8 million tons, accounting for 50% of global production, followed by the Philippines (400,000 tons), New Caledonia (230,000 tons), and Russia (200,000 tons). Other notable producers include Canada, Australia, China, Brazil, and the United States.
Indonesia holds the largest global nickel reserves, reaching 55 million metric tons in 2023 as per USGS, surpassing Australia's 24 million metric tons. With an estimated reserve lifespan of 15 years, Indonesia has become a central player in the global nickel market.
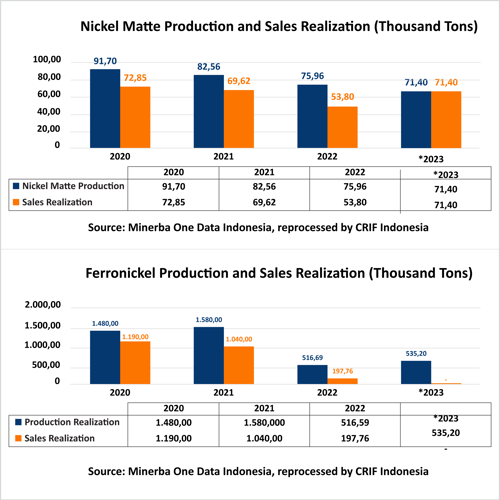
Production and Sales Figures for Nickel Matte and Ferronickel
The metal industry demonstrated robust growth in 2023, achieving a rate of 14.17%. The expansion of nickel matte and ferronickel exports served as a key driver behind the growth of the base metal industry in Indonesia.
An examination of the production trends of these two products reveals that nickel matte production experienced a 6% decrease in 2023, falling from 75,960 tons in 2022 to 71,400 tons. However, nickel matte sales demonstrated a 32.71% increase, rising from 53,800 tons to 71,400 tons. This suggests that the entirety of realized nickel matte production in 2023 was utilized to fulfill the requirements of the domestic nickel industry, with a particular emphasis on the battery sector.
In contrast, ferronickel production in 2022 witnessed a substantial decline of 67.30%, decreasing from 1,580,000 tons to 516,690 tons. This decline can be attributed to a sharp contraction in demand from the steel industry, as the steel sector in Indonesia has encountered developmental challenges.
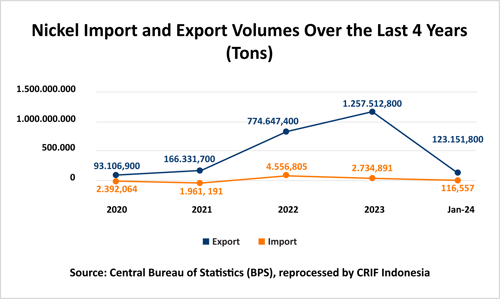
Nickel Exports and Imports in Indonesia
The Indonesian government's emphasis on downstream program development, including the prohibition of raw material exports, has yielded positive outcomes. Notably, export volumes surged by 62.33% in 2023, increasing from 774,647.4 tons in 2022 to 1,257,512.8 tons in 2023.
Conversely, imports declined by 39.98%, decreasing from 4,556,805 tons to 2,734,891 tons. This reduction suggests that Indonesia's nickel industry has successfully mitigated its reliance on foreign nickel raw materials. Nevertheless, considering Indonesia's status as the world's leading nickel producer, achieving zero nickel imports remains a crucial objective for the Indonesian nickel industry.
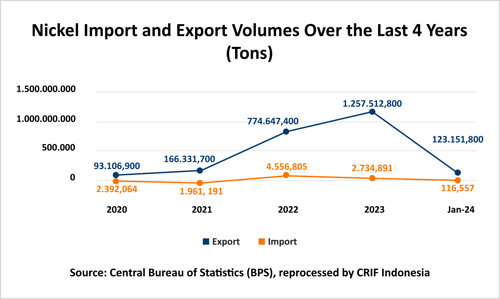
One contributing factor to the sustained import activity is the disruption stemming from raw material supply shortages originating from the Mandiodo Block. This disruption was a consequence of the suspension of mining operations due to a corruption investigation. An additional contributing factor is the necessity to fulfill the demand for high-grade nickel ore, of which the available supply is diminishing.
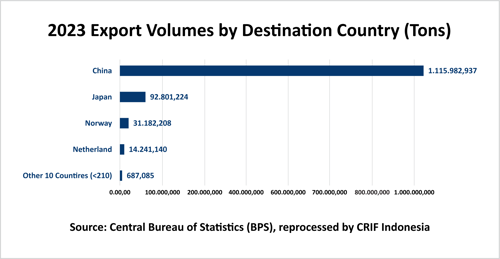
Origins and Destinations of Imports and Exports
Indonesia actively engages in export and import activities with various countries across the globe. In 2023, China emerged as the leading export destination, receiving a substantial volume of 1,115,982.937 tons of Indonesian products, including nickel sulfate, a crucial component in the production of high-nickel-content lithium batteries. Other key export partners include Japan, Norway, the Netherlands, and several more countries.
In 2023, Indonesia's nickel ore imports primarily originated from the Philippines, with volumes reaching tens of thousands of tons. Additional imports of nickel and its concentrates, in smaller quantities ranging from hundreds to thousands of kilograms, were sourced from Australia, Brazil, China, and Singapore, arriving through Soekarno-Hatta, Pulau Obi, and Tanjung Priok.
Analysis of export and import price indices reveals a consistent annual increase in export prices, juxtaposed with a declining import price index. This trend underscores the significant potential of Indonesia's nickel products in the export market.
The observed increase in export prices can be attributed to government regulations mandating downstream processing in the mineral and coal sector, as stipulated by Law Number 3 of 2020, which amends Law Number 4 of 2009 on Mineral and Coal Mining. This law mandates the processing of raw nickel ore before export, resulting in a value increase of up to 14 times. A key focus of nickel downstream processing is its use as a raw material for Electric Vehicle (EV) battery production, with domestic value-added ranging from 470 to 780 times. The Indonesian steel industry is actively strengthening its competitiveness to enhance its position in the global market.
Obstacles and Difficulties Encountered in the Nickel Industry
Despite its significant potential, the nickel industry faces several obstacles and challenges. One pressing concern is the relatively low utilization of the steel industry, both domestically and globally, due to the influx of imported goods.
Another challenge lies in the development of processing and refining plants (smelters). Securing funding and meeting the energy requirements for smelter operations pose significant hurdles. The government is currently facilitating discussions between the State Electricity Company (PLN) and nickel industry players who intend to establish their power plants. To address this, the government has organized meetings between these stakeholders, including banks and PLN, to explore opportunities within the nickel industry.
Land acquisition from local communities presents another obstacle in the development of smelter projects. This necessitates effective social approaches, such as land swaps or business-to-business land leasing agreements.
Furthermore, the technology employed in the industry is a concern. Indonesia currently lags in the adoption of advanced technology, making support from other countries essential. The need for foreign experts who can operate and train local workers in using these technologies is also crucial.
Indonesia's Nickel Industry in the Energy Transition: Future Opportunities
Indonesia's nickel downstream program has significantly strengthened the economy of the base metals industry, demonstrating consistent growth despite various challenges. In 2023, Indonesia became the world's leading nickel producer, contributing 50% of global production and possessing the largest nickel reserves globally. The prohibition on raw material exports has increased the added value of domestic nickel products, particularly as raw materials for electric vehicle batteries. Nevertheless, challenges such as low steel industry utilization, obstacles to smelter development, limited technology, and land acquisition issues necessitate immediate resolution.
CRIF Indonesia highlights several key points to propel further growth in nickel production in Indonesia:
-
Enhancement of Smelter Infrastructure: The government and industry must expedite smelter development by addressing funding and energy challenges through strategic partnerships between industry players, PLN (State Electricity Company), and financial institutions.
-
Investment in Technology and Human Resources: Strengthening international collaboration to access advanced technology and attracting foreign experts to train local workers is essential to support the industry's operations.
-
Increase in Nickel Industry Utilization: The government should tighten control over nickel imports and provide incentives to domestic producers to enhance the competitiveness of products in both local and global markets.
-
Social Approach to Land Acquisition: Adopting more inclusive approaches for land acquisition, through fair compensation or business partnerships, to ensure that smelter project development progresses without social barriers.
-
Export Market Diversification: Reducing dependency on specific export markets by expanding international trade networks for processed nickel products to ensure sustainable global demand.
With a targeted strategy, Indonesia has the potential to maximize its nickel resources to bolster the development of a highly competitive base metal industry, while also providing significant advantages to the national economy. The outlook for Indonesia's nickel industry in 2025 is projected to be very positive, driven by the following factors:
-
Increase in Global Demand
The demand for nickel, a raw material essential for electric vehicle (EV) batteries, is anticipated to continue to rise as the global shift toward clean energy progresses. As the world's largest nickel producer, Indonesia is strategically positioned to fulfill this demand, particularly with a focus on value-added products such as nickel sulfate and battery materials.
-
Reinforcement of Downstreaming
The increasingly mature implementation of downstream will solidify Indonesia's position in the global supply chain. Processed products such as ferronickel, nickel matte, and nickel sulfate are expected to dominate exports, thereby increasing state revenue and reducing reliance on raw material exports.
-
Export Market Diversification
By concentrating on strengthening trade relations with countries such as China, Japan, and the European Union, Indonesia can broaden market access for processed nickel products, thus enhancing global competitiveness.
-
Investment and Supportive Policies
Government regulatory support through the Minerba Law and initiatives to attract foreign investment will be key catalysts in propelling the growth of the nickel industry. Investment in technology and the development of local human resources will also bolster the industry's competitiveness.
With these strategic measures, Indonesia will not only be able to capitalize on the vast potential of nickel but also ensure that its base metal industry remains competitive in the global market and generates long-term positive impacts on the national economy.

